Construction Tolerances: Construction Tolerances
Bed joint tolerances
Let’s face it, the perfect masonry wall probably hasn’t been built. But how good is good enough, when constructing a masonry wall or column? Fortunately, the Masonry Building Code contains specifications (TMS 602) that provide construction tolerances that are well recognized within the industry. Keep in mind that these are minimum requirements and that project specifications may require tighter tolerances. Also note that these tolerances are not applicable to either anchored or adhered veneer.
A logical place to start is the bottom of the wall and the applicable tolerance here is that the bed joint for the first course be at least ¼ inch thick but not more than ¾ inch when the masonry is ungrouted or partially grouted. The maximum first course bed joint thickness is increased to 1 ¼ inch when the first course if fully grouted and supported by a concrete foundation. Unless otherwise noted, bed and head joints are to be 3/8 inch (except for the first course).
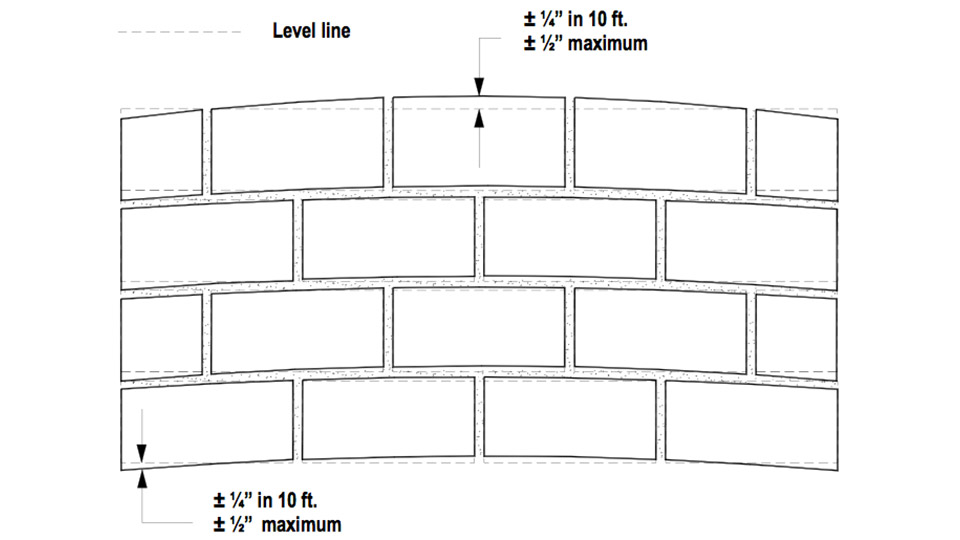
The allowable variation in bed joint thickness between masonry courses is ± 1/8 inch and bed joints are to be within ± ¼ inch of level in 10 feet with a maximum out of level of ½ inch in 10 feet. Note that these apply to CMU and clay masonry construction and that there are other requirements for glass block and autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) masonry.
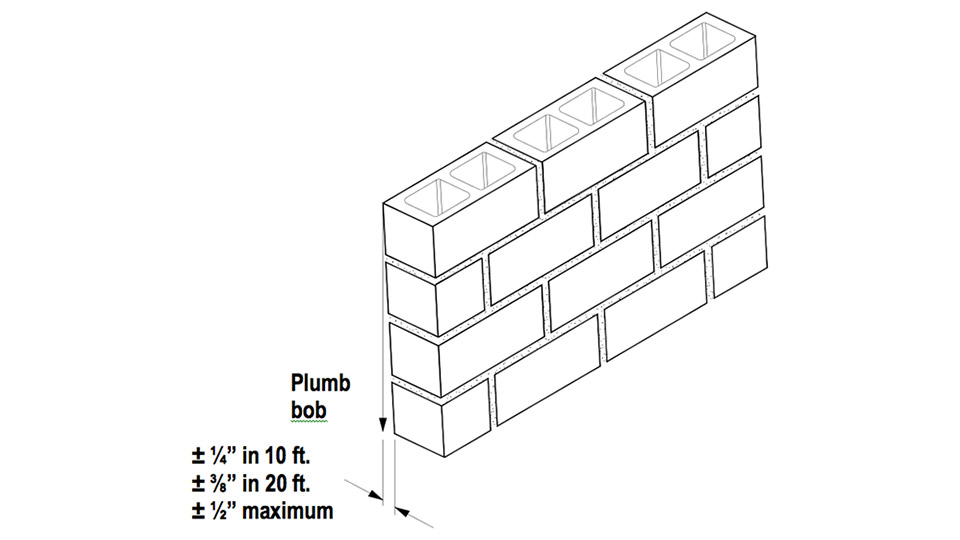
As for overall tolerances for walls, the top surface of load-bearing walls must be within ± ¼ inch of level in 10 feet with a maximum out of level of ½ inch in 10 feet. Plumb tolerances are similar with a permissible variation from plumb of ± ¼ inch in 10 feet, ± 3/8 in 20 feet and ± ½ inch maximum. Walls are to be true to a line with the same tolerances as for plumb.
Plumb tolerance in walls
Load-bearing columns must be within ± ½ inch of plumb from top to bottom and non-load-bearing columns must be within ± ¾ inch of plumb over their height.
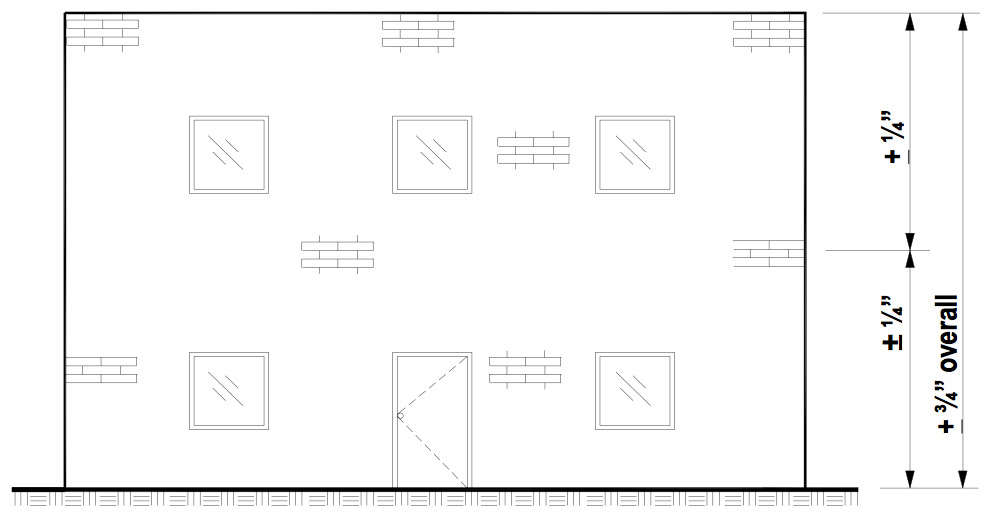
Location of masonry elements in plan must be within ± ½ inch in 20 feet with a maximum variation of ± ¾ inch. Similarly, masonry elements indicated in elevation should be within ± ¼ inch in the story height with a maximum variation of ± ¾ inch.
Tolerances in elevation
Lastly, any aesthetic issues, such as minor chips or cracks, should not be visible when viewed from 20 feet under diffuse lighting. This requirement is not from the Masonry Building Code but is given in ASTM standard specifications for loadbearing CMU (ASTM C90) and for loadbearing brick masonry (ASTM C216). Again, check the project specifications for any additional requirements.